Secondary Memory
The secondary storage devices which are built into the computer or connected to the computer are known as a secondary memory of the computer. It is also known as external memory or auxiliary storage.
The secondary memory is accessed indirectly via input/output operations. It is non-volatile, so permanently stores the data even when the computer is turned off or until this data is overwritten or deleted. The CPU can't directly access the secondary memory. First, the secondary memory data is transferred to primary memory then the CPU can access it.
Some of the secondary memory or storage devices are described below:
1) Hard Disk:
It is a rigid magnetic disc that is used to store data. It permanently stores data and is located within a drive unit.
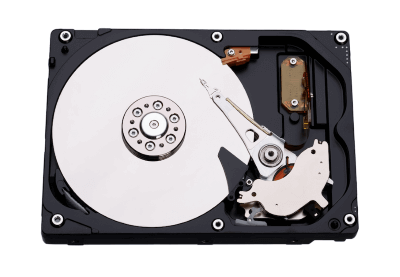
The hard disk is also known as a hard drive. It is a rigid magnetic disc that stores data permanently, as it is a non-volatile storage device. The hard disk is located within a drive unit on the computer's motherboard and comprises one or more platters packed in an air-sealed casing. The data is written on the platters by moving a magnetic head over the platters as they spin. The data stored on a computer's hard drive generally includes the operating system, installed software, and the user's files and programs, including pictures, music, videos, text documents, etc.
Components of Hard Drive:
The main components of a hard drive include a head actuator, read/write actuator arm, read/write head, platter, and spindle. A circuit board, which is called the disk controller or interface board, is present on the back of a hard drive. It allows the hard drive to communicate with the computer.
2) Solid-state Drive:

SSD (Solid State Drive) is also a non-volatile storage medium that is used to hold and access data. Unlike a hard drive, it does not have moving components, so it offers many advantages over SSD, such as faster access time, noiseless operation, less power consumption, and more.
As the cost of SSD has come down, it has become an ideal replacement for a standard hard drive in desktop and laptop computers. It is also suitable for notebooks, and tablets that don't require lots of storage.
3) Pen drive:

Pen drive is a compact secondary storage device. It is also known as a USB flash drive, thumb drive or a jump drive. It connects to a computer via a USB port. It is commonly used to store and transfer data between computers. For example, you can write a report using a computer and then copy or transfer it in the pen drive. Later, you can connect this pen drive to a computer to see or edit your report. You can also store your important documents and pictures, music, videos in the pen drive and keep it at a safe place.
Pen drive does not have movable parts; it comprises an integrated circuit memory chip that stores the data. This chip is housed inside a plastic or aluminium casing. The data storage capacity of the pen drive generally ranges from 2 GB to 128 GB. Furthermore, it is a plug and play device as you don't need additional drives, software, or hardware to use it.
4) SD Card:

SD Card stands for Secure Digital Card. It is most often used in portable and mobile devices such as smartphones and digital cameras. You can remove it from your device and see the things stored in it using a computer with a card reader.
There are many memory chips inside the SD card that store the data; it does not have moving parts. SD cards are not created equal, so they may differ from each other in terms of speed, physical sizes, and capacity. For example, standard SD cards, mini SD cards, and micro SD cards.
5) Compact Disk (CD):

Compact Disk is a portable secondary storage device in the shape of a round medium disk. It is made of polycarbonate plastic. The concept of CD was co-developed by Philips and Sony in 1982. The first CD was created on 17 August 1982 at the workshop of Philips in Germany.
In the beginning, it was used for storing and playing sound recordings, later it was used for various purposes such as for storing documents, audio files, videos, and other data like software programs in a CD.Physical characteristics of a CD/ Structure of CD:
A standard CD is around 5 inches in diameter and 0.05 inches in thickness. It is made of a clear polycarbonate plastic substrate, a reflective metallic layer, and a clear coating of acrylic plastic. These thin circular layers are attached one on top of another as described below:
- A polycarbonate disc layer at the bottom has the data encoded by creating lands and pits.
- The polycarbonate disc layer is coated with a thin aluminium layer that reflects the laser.
- The reflective aluminium layer is coated with a lacquer layer to prevent oxidation in order to protect the below layers. It is generally spin coated directly on the top of the reflective layer.
- The label print is applied on the lacquer layer, or artwork is screen printed on the top of the disc on the lacquer layer by offset printing or screen printing.
How Does a CD Work?
The data or information is stored or recorded or encoded in CD digitally using a laser beam that etches tiny indentations or bumps on its surface. The bump is called a pit, which represents the number 0. Space, where the bump is not created, is called land, and it represents the number 1. Thus, the data is encoded into a compact disc by creating pits (0) and lands (1). The CD players use laser technology to read the optically recorded data.
6) DVD:

DVD is short for digital versatile disc or digital video disc. It is a type of optical media used for storing optical data. Although it has the same size as a CD, its storage capacity is much more than a CD. So, it is widely used for storing and viewing movies and to distribute software programs as they are too large to fit on a CD. DVD was co-developed by Sony, Panasonic, Philips, and Toshiba in 1995.
Types of DVDs:
DVDs can be divided into three main categories which are as follows:
- DVD-ROM (Read-Only): These types of DVDs come with media already recorded on them, such as movie dvds. As the name suggests, data on these discs cannot be erased or added, so these discs are known as a read-only or non-writable DVD.
- DVD-R (Writable): It allows you to record or write information to the DVD. However, you can write information only once as it becomes a read-only DVD once it is full.
- DVD-RW (Rewritable or Erasable): This type of discs can be erased, written, or recorded multiple times.



0 Comments